Introduction: Why Silybin B vs. Silymarin Still Confuses the Market
If you work in nutraceuticals, functional foods, or botanical ingredient sourcing, you’ve likely seen Silymarin and Silybin used interchangeably. In reality, they are not the same thing, and the distinction matters—especially for formulation accuracy, regulatory compliance, and long-term supply consistency.

This article breaks down Silybin B vs. Silymarin in plain, professional language. We’ll look at what each ingredient really is, how they differ in composition and use, and why more manufacturers are shifting toward high-purity Silybin B powder for standardized products.
The goal is simple: help buyers, R&D teams, and brand owners make better sourcing and formulation decisions.
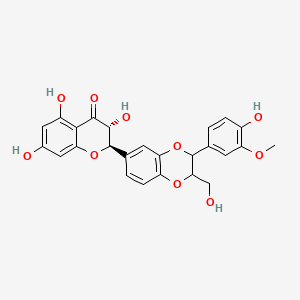
1. What Is Silymarin?
Silymarin is not a single compound. It is a complex mixture of flavonolignans extracted from the seeds of Silybum marianum (milk thistle).

Typical silymarin extracts contain:
- Silybin A
- Silybin B
- Isosilybin A & B
- Silychristin
- Silydianin
In commercial terms, silymarin is usually standardized to 70–80% total flavonolignans, not to one specific molecule.
Practical implications for manufacturers
- Composition varies by extraction method and raw material quality
- Batch-to-batch consistency can be harder to control
- Best suited for traditional botanical supplements, not precision formulations
This is why many R&D teams now ask a more specific question: Which silymarin component actually matters most?
2. What Is Silybin B?
Silybin B is a single, well-defined flavonolignan and one of the main active components within silymarin. Chemically, it is a diastereomer of Silybin A, meaning both share the same molecular formula but differ in spatial structure.
Key identifiers:
- CAS No.: 22888-70-6
- Molecular weight: 482.44 g/mol
- Typically supplied at ≥98% purity (HPLC)
Unlike mixed silymarin extracts, Silybin B offers clarity and control. For manufacturers, that means predictable behavior in formulations and easier documentation for quality systems.
👉 Learn more about high-purity Silybin B powder and bulk sourcing here:
https://aiherba.com/silybin-b/
3. Silybin B vs. Silymarin: A Side-by-Side Comparison
| Feature | Silymarin | Silybin B |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Multi-component extract | Single isolated compound |
| Standardization | Total flavonolignans | Specific molecule |
| Batch consistency | Moderate | High |
| Analytical control | Limited | Precise (HPLC) |
| Typical use | Traditional supplements | Modern nutraceuticals, R&D |
| Formulation flexibility | Medium | High |
From a B2B sourcing perspective, this difference alone often determines which ingredient is the better fit.
4. Functional Properties: How the Two Are Used (Non-Medical)
Both ingredients are widely studied for their antioxidant-related properties, but they are used differently in practice.
Silymarin
- Broad-spectrum botanical extract
- Common in legacy formulations
- Suitable when traditional positioning matters
Silybin B
- Used as a reference compound in research
- Preferred when formulations require precision
- Often selected for premium or science-driven products
Importantly, these uses relate to ingredient functionality, not disease treatment. Any health-related positioning must follow local regulatory frameworks.
5. Why Purity and Standardization Matter in Modern Formulation
As regulations tighten and global markets demand transparency, many brands are moving away from loosely defined extracts.
Choosing Silybin B as a bulk ingredient offers:
- Easier specification control
- Cleaner COA and safety documentation
- Better alignment with GMP and ISO systems
For contract manufacturers and global brands, this can reduce compliance risk and simplify cross-market approvals.
👉 For buyers evaluating suppliers, reviewing a Silybin B spec sheet and COA is now standard practice.
https://aiherba.com/silybin-b/
6. Regulatory & Industry Perspective
From a regulatory standpoint, both silymarin and Silybin B are treated as botanical ingredients, not pharmaceutical drugs.
Relevant authorities and references:
- FDA (Dietary Supplement Ingredient Guidance) – https://www.fda.gov
- NIH – Office of Dietary Supplements – https://ods.od.nih.gov
- European Medicines Agency (EMA) herbal monographs
Using a single, well-characterized compound like Silybin B can make internal quality reviews and external audits more straightforward.
7. Which Should Manufacturers Choose?
There’s no universal answer—but there is a practical one.
- Choose Silymarin if your product emphasizes tradition and whole-plant extracts
- Choose Silybin B if your priorities are:
- Precision
- Consistency
- Scientific positioning
- Long-term bulk supply reliability
For many modern nutraceutical brands, Silybin B aligns better with current market expectations.
FAQ: Common Buyer Questions
1. Is Silybin B the same as Silymarin?
No. Silymarin is a mixture; Silybin B is a single purified compound.
2. Why do some suppliers prefer Silybin B?
Because it offers better batch consistency and clearer specifications.
3. Can Silybin B be used in dietary supplements?
Yes, as a botanical ingredient, subject to local regulations.
4. Is Silybin B more expensive than Silymarin?
Typically yes, due to higher purity and additional processing—but it can reduce formulation risk.
5. What documents should a Silybin B supplier provide?
COA, MSDS/SDS, specification sheet, and testing methods (HPLC).
6. Where can I source Silybin B in bulk?
From GMP-certified manufacturers offering traceable raw materials and third-party testing, such as:
https://aiherba.com/silybin-b/
References & Scientific Sources
- PubMed – Research on silymarin and silybin flavonolignans
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov - NIH – Dietary Supplement Fact Sheets
https://ods.od.nih.gov - U.S. FDA – Botanical and dietary ingredient guidance
https://www.fda.gov - European Medicines Agency – Herbal monographs
https://www.ema.europa.eu
Bulk Supply & Technical Support
Get direct factory quotes, COA, and MSDS within 12 hours. We support bulk supply and custom specifications.
