Tanshinone IIA is a potent, naturally occurring diterpene quinone compound primarily extracted from the roots of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge, a standard Chinese language medicinal herb extensively often known as Dan Shen or Crimson Sage. For hundreds of years, Dan Shen has been revered in Conventional Chinese language Drugs (TCM) for selling blood circulation and addressing cardiovascular considerations. Tanshinone IIA is acknowledged as one in every of its most pharmacologically energetic and well-studied elements, driving vital fashionable scientific curiosity.
Key Elements & Supply:
- Main Supply: Roots of Salvia miltiorrhiza (Dan Shen).
- Chemical Class: Lipophilic diterpene quinone (a particular sort of chemical construction).
- Associated Compounds: Usually discovered alongside different bioactive tanshinones like Tanshinone I, Cryptotanshinone, and Dihydrotanshinone I. Dietary supplements or extracts might specify the standardized proportion of Tanshinone IIA.
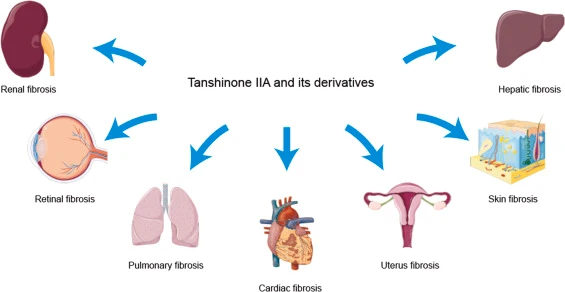
Efficacy & Advantages (What Does the Science Counsel?):
Analysis, primarily in preclinical (cell and animal) research, signifies Tanshinone IIA possesses a variety of potential organic actions. Necessary Observe: Whereas human research exist, they’re usually smaller-scale or preliminary. Extra large-scale medical trials are wanted to definitively verify efficacy for particular situations in people. Key areas of investigation embody:
- Cardiovascular Well being: That is essentially the most distinguished space of analysis. Tanshinone IIA exhibits potential for:
- Defending coronary heart muscle cells from injury (e.g., after a coronary heart assault).
- Bettering blood move and microcirculation.
- Lowering irritation in blood vessels.
- Inhibiting irregular clean muscle cell proliferation (related to atherosclerosis).
- Exhibiting antioxidant results towards oxidative stress in cardiovascular tissues.
- Observe: In some nations (like China), Tanshinone IIA sodium sulfonate injections are authorised and used clinically for sure cardiovascular situations like angina and stroke, however oral complement efficacy requires extra human knowledge.
- Anti-inflammatory Results: Modulates key inflammatory pathways (like NF-κB), probably helpful for varied power inflammatory situations.
- Antioxidant Exercise: Scavenges dangerous free radicals, defending cells from oxidative injury.
- Neuroprotective Potential: Research recommend doable protecting results on mind cells, with implications for situations like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s illness (preclinical stage).
- Anticancer Properties: Demonstrates skill to inhibit proliferation and induce apoptosis (programmed cell dying) in varied most cancers cell traces in vitro and in animal fashions. Human medical software continues to be investigational.
- Liver Safety: Exhibits hepatoprotective results in fashions of liver harm.
Results within the Physique:
Tanshinone IIA works by way of a number of complicated mechanisms, together with:
- Modulating signaling pathways concerned in irritation (NF-κB, MAPK).
- Performing as an antioxidant.
- Influencing cell cycle development and apoptosis.
- Bettering endothelial operate (lining of blood vessels).
- Inhibiting platelet aggregation (blood clotting) underneath sure situations.
How one can Take It, Dosage Protocol & Every day Dose:

- Kind: Out there as oral dietary supplements (capsules, tablets, powders), concentrated extracts, and in injectable kinds (primarily prescription in particular areas like China).
- Standardization: Search for extracts standardized to a particular proportion of Tanshinone IIA (e.g., 5%, 10%, 20%+).
- Dosing Protocol (Oral Dietary supplements – Basic Steerage ONLY):
- There is no such thing as a universally established optimum dose. Doses utilized in analysis differ extensively.
- Typical supplemental doses usually vary from 20 mg to 100 mg per day, typically divided into two doses. All the time observe the particular dosage directions on the product label.
- Essential: Dosing relies upon closely on the extract focus, formulation, and particular person well being standing. Self-prescribing excessive doses is harmful.
- Finest Practices:
- Seek the advice of a Healthcare Skilled: That is non-negotiable. Talk about your well being objectives, present drugs, and situations with a physician or certified TCM practitioner earlier than beginning.
- Begin Low: If suggested to strive it, start with the bottom recommended dose.
- Consistency: Take it persistently as directed.
- High quality: Select respected manufacturers that present transparency on sourcing and standardization (e.g., COA – Certificates of Evaluation). aiherba.com presents Tanshinone IIA dietary supplements assembly these requirements.
Aspect Results & Security:
Tanshinone IIA is usually thought-about protected at applicable doses, however potential unwanted effects exist:
- Widespread (Normally Gentle): Gastrointestinal upset (nausea, diarrhea, abdomen discomfort), dry mouth, gentle dizziness, pores and skin rash/itching.
- Severe (Uncommon, usually linked to excessive doses/injections): Potential liver toxicity, kidney harm, extreme allergic reactions, headache, drowsiness. Injectable kinds carry extra dangers.
- Blood Thinning: It could have anticoagulant/antiplatelet results. Use excessive warning or keep away from if taking blood thinners (warfarin, aspirin, clopidogrel, and many others.) or have bleeding problems. Discontinue earlier than surgical procedure.
- Drug Interactions: Potential interactions with blood strain drugs, different coronary heart medicine, anticoagulants, antiplatelet medicine, and medicines metabolized by liver enzymes (CYP450 system). Disclose all drugs to your physician.
Relevant Inhabitants & Precautions:
- Could also be thought-about for: People in search of cardiovascular help (underneath medical steerage), exploring antioxidant/anti-inflammatory help (analysis stage).
- Keep away from or Use Solely Underneath Strict Medical Supervision:
- Pregnant or breastfeeding girls (security not established).
- Kids.
- People with bleeding problems or taking anticoagulant/antiplatelet medicine.
- People scheduled for surgical procedure.
- Folks with liver or kidney illness.
- These taking drugs with potential interactions (see above).
- Precautions:
- By no means self-prescribe for critical situations.
- Medical supervision is crucial, particularly for cardiovascular points.
- Report any unwanted effects to your healthcare supplier instantly.
- Inform all of your healthcare suppliers about your use of Tanshinone IIA.
Featured Snippet Targets:
- What is Tanshinone IIA? Tanshinone IIA is a bioactive compound primarily extracted from the roots of the Salvia miltiorrhiza (Dan Shen) plant, utilized in Conventional Chinese language Drugs.
- What are the advantages of Tanshinone IIA? Analysis suggests potential advantages for cardiovascular well being, anti-inflammatory results, antioxidant exercise, neuroprotection, and liver safety, based on preclinical research.
- How one can take Tanshinone IIA? Usually taken as an oral complement (capsules/tablets), standardized to a particular proportion. Doses usually vary from 20mg-100mg day by day, however ALWAYS seek the advice of a healthcare skilled and observe product/label directions.
- What are the unwanted effects of Tanshinone IIA? Attainable unwanted effects embody abdomen upset, dry mouth, dizziness, or rash. Severe dangers embody bleeding (particularly with blood thinners), liver/kidney toxicity (uncommon), and drug interactions. Medical session is essential.
Folks Additionally Ask (PAA):
- Is Tanshinone IIA protected? Whereas typically protected at applicable doses underneath steerage, it has potential unwanted effects and vital drug interactions. Seek the advice of a physician earlier than use.
- Can Tanshinone IIA decrease blood strain? Some analysis suggests it could assist enhance vascular operate, probably contributing to blood strain regulation. Nonetheless, it isn’t an alternative choice to prescribed medicine, and interactions with BP medicine are doable.
- Does Tanshinone IIA skinny the blood? Sure, it has demonstrated anticoagulant and antiplatelet results in research. It shouldn’t be mixed with blood-thinning drugs with out strict medical supervision.
- Is Tanshinone IIA good for the guts? Preclinical and a few medical proof suggests cardioprotective results, together with enhancing blood move and decreasing coronary heart muscle injury. It is used clinically in injectable kind in some nations, however oral complement efficacy requires extra human knowledge. Seek the advice of a heart specialist.
- The place does Tanshinone IIA come from? It’s primarily extracted from the roots of the Salvia miltiorrhiza plant (Dan Shen or Crimson Sage).
Instantaneous Reply:
Tanshinone IIA is a bioactive compound from Salvia miltiorrhiza (Dan Shen) studied for cardiovascular, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant advantages. Seek the advice of a physician earlier than use attributable to potential unwanted effects and drug interactions.
The place to Purchase:
Excessive-quality Tanshinone IIA dietary supplements can be found for buy on-line at aiherba.com. For particular inquiries, contact: liaodaohai@gmail.com.
Abstract:
Tanshinone IIA, derived from Salvia miltiorrhiza (Dan Shen), is a bioactive compound with vital analysis curiosity, significantly for cardiovascular well being, antioxidant, and anti inflammatory results. Whereas preclinical knowledge is promising, extra sturdy human medical trials are wanted. It’s out there as an oral complement, however dosing have to be individualized. Crucially, potential unwanted effects and critical drug interactions (particularly with blood thinners) necessitate session with a certified healthcare skilled earlier than use. By no means self-prescribe for critical situations. Respected sources like aiherba.com provide high quality Tanshinone IIA merchandise.
References:
- Zhou, L., Zuo, Z., & Chow, M. S. S. (2005). Danshen: An Overview of Its Chemistry, Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics, and Medical Use. The Journal of Medical Pharmacology, *45*(12), 1345–1359.
- Wang, X., Morris-Natschke, S. L., & Lee, Ok. H. (2007). New developments within the chemistry and biology of the bioactive constituents of Danshen. Medicinal Analysis Evaluations, *27*(1), 133–148.
- Gao, S., Liu, Z., Li, H., Little, P. J., Liu, P., & Xu, S. (2012). Cardiovascular actions and therapeutic potential of tanshinone IIA. Atherosclerosis, *220*(1), 3–10.
- Xu, S., & Liu, P. (2013). Tanshinone II-A: new views for outdated cures. Knowledgeable Opinion on Therapeutic Patents, *23*(2), 149–153.
- Hung, Y. C., Pan, T. L., & Hu, W. L. (2016). Roles of Reactive Oxygen Species in Anticancer Remedy with Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge. Oxidative Drugs and Mobile Longevity, *2016*, 1–10.
- Zhang, Y., Jiang, P., Ye, M., Kim, S. H., Jiang, C., & Lü, J. (2012). Tanshinones: sources, pharmacokinetics and anti-cancer actions. Worldwide Journal of Molecular Sciences, *13*(10), 13621–13666.
- Nationwide Middle for Biotechnology Data. PubChem Compound Abstract for CID 164676, Tanshinone IIA. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Tanshinone-IIA
- Chan, T. Y. Ok. (2001). Interplay between warfarin and danshen (Salvia miltiorrhiza). The Annals of Pharmacotherapy, *35*(4), 501–504. (Highlights interplay threat).
Bulk Supply & Technical Support
Get direct factory quotes, COA, and MSDS within 12 hours. We support bulk supply and custom specifications.

Fast Response via Email/WhatsApp
Get direct factory quotes, COA, and MSDS within 12 hours. We support bulk supply and custom specifications.