Introduction: Why Ergothioneine Is Gaining Attention in Functional Formulations
Ergothioneine is increasingly recognized by formulators and ingredient buyers as a unique naturally occurring antioxidant amino acid, distinct from conventional antioxidants such as vitamin C or polyphenols.
Rather than acting as a short-lived radical scavenger, ergothioneine functions as a cellular protective compound, selectively accumulated in human tissues exposed to oxidative stress. This unique biological behavior has driven growing interest in ergothioneine as a functional ingredient for dietary supplements, functional foods, and cosmetic formulations.
This guide is written specifically for manufacturers, formulators, and procurement professionals, providing a science-based overview while addressing practical sourcing, quality, and regulatory considerations.
What Is Ergothioneine?
Ergothioneine (EGT) is a naturally occurring sulfur-containing amino acid derivative, synthesized by certain fungi and bacteria. Humans do not produce ergothioneine endogenously; it is obtained exclusively through diet or supplementation.

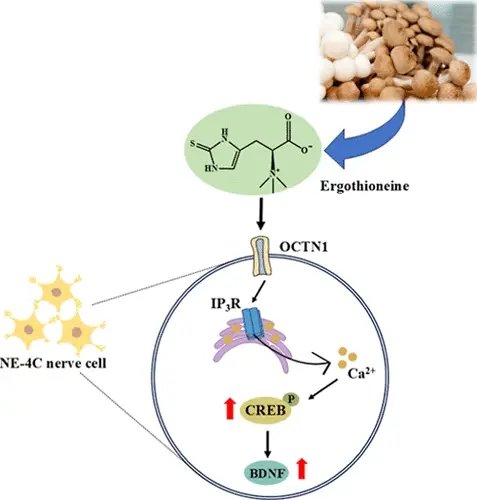
Notably, ergothioneine is actively transported into cells via the OCTN1 transporter, a highly specific uptake mechanism that suggests an important physiological role.
Key characteristics:
- Water-soluble amino acid derivative
- High stability under physiological conditions
- Selective cellular accumulation
- Resistant to rapid oxidation
How Ergothioneine Works: Mechanisms Supported by Research
Unlike general antioxidants that are rapidly consumed, ergothioneine demonstrates long-term cellular persistence.
Mechanistic Highlights
- Selective uptake through OCTN1 transporter
- Accumulation in mitochondria, liver, brain, and erythrocytes
- Acts as a redox buffer rather than a single-use antioxidant
- Supports cellular resilience against oxidative stress
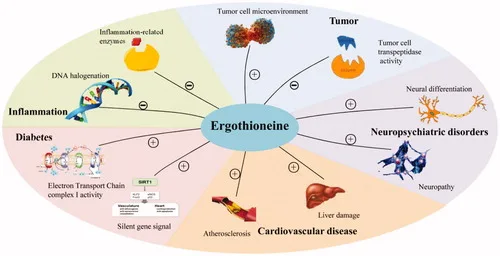
Several studies suggest ergothioneine plays a role in cellular homeostasis, especially in tissues subject to chronic oxidative exposure.
From a formulation perspective, this mechanism makes ergothioneine particularly attractive for daily-use products, where stability and sustained activity are valued.
Scientific Evidence and Safety Profile
Research Landscape
Over the past decade, ergothioneine has been widely studied in:
- Nutritional biochemistry
- Cellular aging research
- Oxidative stress models
Epidemiological data has also associated dietary ergothioneine intake with markers of long-term health resilience, without positioning it as a therapeutic agent.
Safety & Regulatory Status
- Recognized as GRAS (Generally Recognized As Safe) in the United States for specific uses
- Used in dietary supplements and cosmetic formulations in multiple global markets
- Favorable toxicological profile in published studies
Importantly for manufacturers, ergothioneine is considered a low-risk functional ingredient when used within established formulation ranges.
Applications Across Industries
Dietary Supplements
- Capsule and tablet formulations
- Daily antioxidant blends
- Longevity-positioned products (non-medical claims)
Functional Foods & Beverages
- Nutritional powders
- Ready-to-mix functional drinks
- Stability-focused formulations
Cosmetic & Personal Care
- Skin barrier support formulations
- Anti-pollution cosmetic products
- Oxidative stress protection positioning
Ergothioneine as a B2B Ingredient: What Buyers Look For
For professional buyers, ergothioneine sourcing decisions go beyond benefits alone.
Typical Procurement Considerations
| Factor | What Buyers Evaluate |
|---|---|
| Purity | ≥98% or ≥99% assay |
| Testing | HPLC, residual solvents |
| Compliance | cGMP, ISO, COA |
| Supply | Stable production capacity |
| MOQ | Flexible bulk quantities |
| Documentation | Full traceability |
Quality Specifications and Manufacturing Standards
High-quality ergothioneine ingredient suppliers typically provide:
- Assay Method: HPLC
- Appearance: White to off-white powder
- Solubility: Water-soluble
- Stability: Excellent under standard storage conditions
- Documentation: COA, MSDS, specification sheet
For manufacturers, consistency between batches is often more critical than theoretical purity alone.
Bulk Supply, OEM & Private Label Considerations
When sourcing ergothioneine for commercial use, buyers should assess:
- Raw material traceability
- Production scalability
- OEM/ODM formulation support
- Regulatory experience in target markets
👉 Learn more about AIHerba’s GMP manufacturing and OEM/ODM capabilities:
https://aiherba.com/our-factory-gmp-production-advanced-extraction-oem-odm-services/
Why Work With an Established Ergothioneine Supplier?
An experienced supplier does more than deliver raw material. They support:
- Formulation feasibility
- Regulatory documentation
- Stable long-term supply
- Technical communication
👉 View AIHerba’s ingredient portfolio:
https://aiherba.com/ingredients/
👉 Explore finished product and customization options:
https://aiherba.com/products/
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is ergothioneine a vitamin?
No. Ergothioneine is an amino acid derivative, not classified as a vitamin.
Is ergothioneine suitable for long-term use?
Published research indicates a favorable safety profile when used within standard formulation ranges.
What purity level is recommended for supplements?
Most commercial formulations use ≥98% purity ergothioneine.
Can ergothioneine be used in cosmetics?
Yes, ergothioneine is widely used in cosmetic formulations focused on oxidative stress protection.
Is ergothioneine synthetic or natural?
Commercial ergothioneine may be produced via controlled fermentation or synthetic processes, depending on supplier.
Looking for a Reliable Ergothioneine Ingredient Partner?
If you are sourcing ergothioneine for supplement, food, or cosmetic manufacturing, our technical team can support you with specifications, compliance documentation, and bulk supply solutions.
👉 Contact our team for bulk ingredient inquiries
👉 Request technical documentation or samples
(Inquiry-based, not Add-to-Cart)
★★★★★
“Clear technical information and responsive support. We evaluated multiple ergothioneine suppliers, and AIHerba stood out for documentation and consistency.”
— Procurement Manager, EU Nutraceutical Company
References
- PubMed – Ergothioneine transport and function
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - NIH – Antioxidant amino acid research
https://www.nih.gov/ - FDA – GRAS Notices
https://www.fda.gov/food/generally-recognized-safe-gras - EFSA – Novel food & ingredient safety
https://www.efsa.europa.eu/
Bulk Supply & Technical Support
Get direct factory quotes, COA, and MSDS within 12 hours. We support bulk supply and custom specifications.

Fast Response via Email/WhatsApp
Get direct factory quotes, COA, and MSDS within 12 hours. We support bulk supply and custom specifications.