Table of Contents
In today’s era of “anti-aging first”, everyone is eager to slow down the pace of aging. Recently, AKG, PQQ and ergothioneine, three anti-aging ingredients, have attracted much attention. Today, let’s take a deeper look at their working principles, clinical evidence, and the inextricable connection between them and anti-aging.
AKG The “bright new star” of anti-aging
AKG, as one of the important metabolites of the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, plays a pivotal role in many key activities of cells. It participates in cellular energy metabolism and provides energy support for various life activities of cells; it is also indispensable in the process of amino acid and protein synthesis, and is the basis for maintaining the normal physiological function of cells; at the same time, it is also involved in epigenetic regulation, affecting gene expression, and is of great significance to the differentiation of stem cells and fertility and reproductive health, and even has a certain role in regulating the behavior of cancer cells.
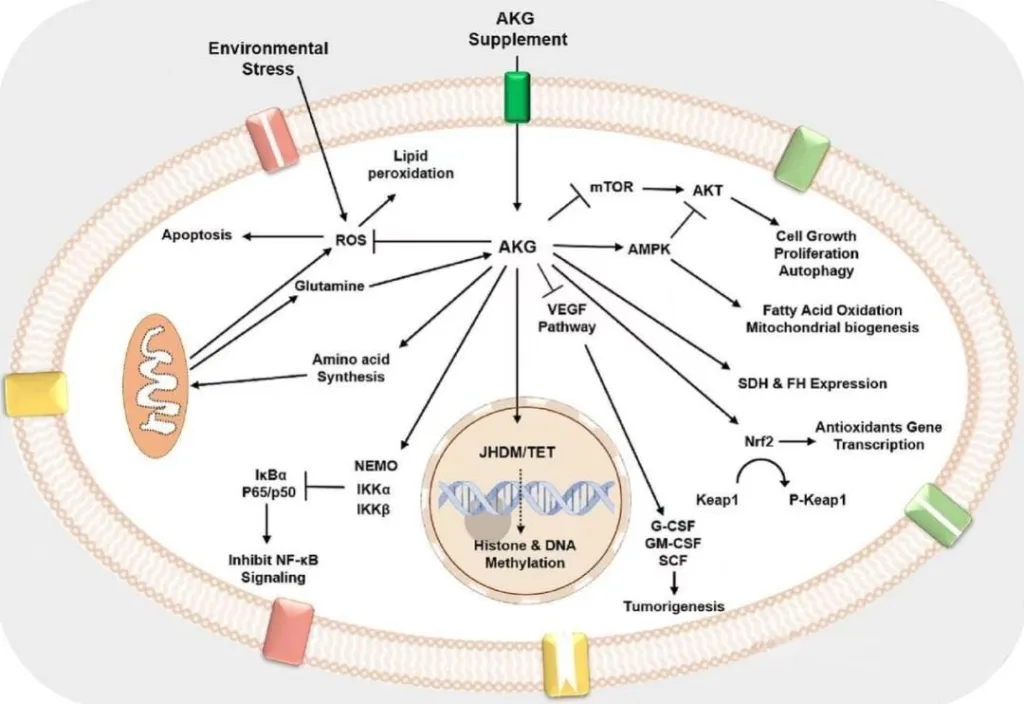
▲In cell metabolism, various metabolic pathways are involved in the formation and dissociation of AKG
In a clinical study in 2021, participants took AKG mixed supplements for an average of 7 months (ranging from 4 to 10 months), and DNA methylation testing found that their physiological age was reduced by an average of 8 years. In addition, the study also found two interesting phenomena: First, the more aged the participants were, the more significant the effect of taking AKG was. In layman’s terms, people who look older than their peers will have a more obvious age reduction effect after taking AKG; second, men have a more prominent age reduction effect after taking AKG than women.
In addition to reducing age, a review report in 2023 pointed out that AKG can promote skin hydration and make the skin more tender; it also has a strong antioxidant capacity, which can promote the discharge of ROS (reactive oxygen species) and reduce the damage of free radicals to cells; in terms of postoperative rehabilitation, AKG can also play a positive role in helping patients improve their quality of life. These magical effects are not only due to its antioxidant capacity, but also because AKG can support stem cell function, allowing the body to continuously produce younger cells, while enhancing the function of immune cells and improving the body’s resistance.

▲AKG reduces the methylation age of homogeneous subgroups
It is worth mentioning that in the daily diet of humans, the amount of naturally occurring AKG is very small and can be ignored, so directly supplementing AKG has become the only effective way to ingest it. AKG also has an advantage. It is highly water-soluble, which makes it easily absorbed after entering the human body and can be almost completely utilized by the body, and will not be easily excreted with excrement. In addition, AKG performs well in controlling metabolic disorders and can improve insulin resistance, which is much better than the popular “anti-aging boss” rapamycin in previous years, because rapamycin may cause insulin resistance.
In summary, AKG has significant effects in promoting muscle growth, accelerating wound healing, improving cell energy status, enhancing immunity, and helping postoperative recovery due to its antioxidant, stem cell and immune cell support properties. For women, it can also make the skin more tender and improve fertility.
PQQ The loyal guardian of cell energy
PQQ is a new type of cofactor with similar physiological functions to vitamins. It can be found in many common foods, such as fermented soybeans, natto, green peppers, kiwis, parsley, tea, papaya, spinach, celery, and even breast milk.
The biological functions of PQQ are mainly reflected in two key aspects: First, it supports the growth and development of mitochondria. As the “energy factory” of cells, the function of mitochondria is directly related to human energy. PQQ can help mitochondria work better and provide sufficient energy for cells; second, it has excellent antioxidant properties, can scavenge free radicals, reduce cell damage, and protect cells from free radicals.
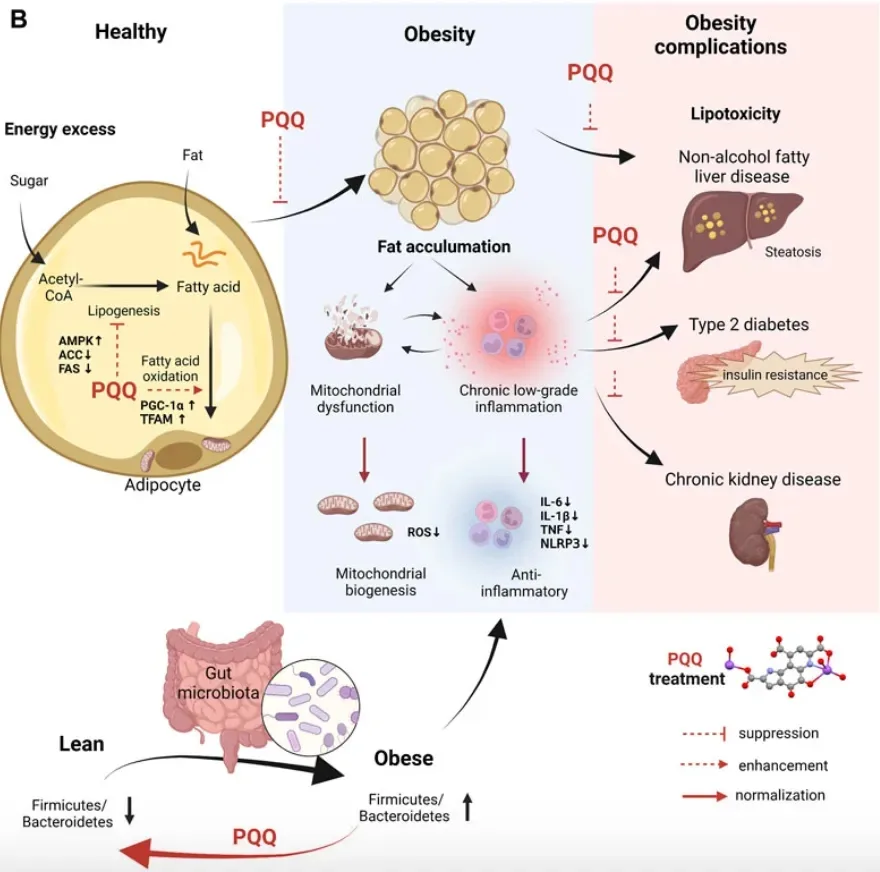
▲It has good antioxidant, free radical scavenging and cell damage reduction effects
Based on these two functions, PQQ plays an important role in many health fields. In terms of improving muscle mass, strength and motor function, a double-blind controlled clinical trial showed that taking PQQ supplements for 12 weeks can help maintain muscle strength, quality and physical activity, which is undoubtedly good news for people who love fitness, bodybuilding and sports.
The specific principles are as follows: In terms of anti-fatigue, PQQ promotes energy production by participating in the TCA cycle, making people full of energy; it can also increase the content of NAD+, thereby enhancing the activity of sirtuin 1 (SIRT1), and SIRT1 can promote the production of mitochondria, which makes it easy to understand why taking PQQ can improve energy and muscle mass; in terms of anti-inflammatory, PQQ can inhibit inflammatory cytokines in skeletal muscle, reduce muscle atrophy, and inhibit the decomposition of muscle protein, thereby maintaining muscle strength and physical function; at the same time, PQQ can also remove reactive oxygen species (ROS) in skeletal muscle, further inhibiting muscle atrophy.
In terms of improving brain cognition, another randomized double-blind controlled trial found that taking PQQ for 12 weeks continuously improved cognitive abilities of both young and old people, specifically in terms of compound memory, verbal memory, cognitive flexibility, processing speed and execution speed. For young people, it can improve learning and work efficiency, and for the elderly, it can help prevent dementia.
In addition, PQQ also performs well in restoring mitochondrial health and improving metabolism. It can repair damaged mitochondrial function and reduce fat accumulation, especially liver fat and visceral fat, which have a greater impact on health. This is a powerful “assist” for people who pursue a good figure and focus on weight loss.
▲PQQ can reduce fat accumulation and improve obesity.
In addition to these clinically proven functions, PQQ still needs to be further confirmed in some aspects. For example, it was found in mouse experiments that it may prevent senile osteoporosis; in in vivo and in vitro cell experiments, it was found that it has a certain effect on improving eye health and protecting retinal ganglion cells; in mouse experiments, it was also observed that it can regulate intestinal flora and thyroid function; in rat experiments, it has an effect on improving pulmonary hypertension; in human cell experiments, it shows the potential to delay cell aging; in mouse experiments, it is found to help prevent ovarian aging and maintain fertility.
Ergothioneine (EGT)
The new king in the field of antioxidants
Ergothioneine (EGT) is a rare natural amino acid, mainly produced by edible fungi represented by Ganoderma lucidum. Since the human body cannot synthesize it by itself, its status in the human body is somewhat similar to vitamins and needs to be obtained from the outside.
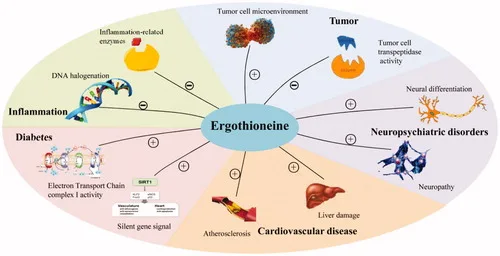
▲ Ergothioneine can affect Sirtuins and KEAP 1-NRF 2 pathways, so it is not only an antioxidant, but also an anti-aging agent.
Ergothioneine has many powerful functions. It can remove free radicals, detoxify, maintain DNA biosynthesis, ensure normal cell growth and cellular immunity, and has anti-radiation and whitening effects. In 2018, it was included in the EU’s new resource food list. In recent years, more and more evidence has shown that a diet rich in ergothioneine may help prolong life, so it is also called the “longevity vitamin” by anti-aging enthusiasts.
The mechanism of action of EGT is very unique. It is not only a direct antioxidant itself, but also can regulate the entire antioxidant system and increase the expression of antioxidant genes. In aging cells, free radicals such as ROS and RNS will increase, leading to the loss of activity of the longevity protein Sirtuin. EGT is like a “scavenger” of free radicals, which can remove ROS and RNS, and it can also enhance the activity of Sirtuins by preventing the oxidative modification of Sirtuin enzymes with the help of NAD+. At the same time, ergothioneine also affects Sirtuins and KEAP1-NRF2 pathways, so it is not only an antioxidant, but also a good anti-aging player.
In the human body, there are two parts that are particularly sensitive to changes in ergothioneine concentrations. The first is the brain, which is a highly active organ in human energy metabolism and is easily affected by oxidative stress and inflammatory responses. The accumulation of ergothioneine in the brain may help resist oxidative damage, inflammatory responses, and prevent mitochondrial function decline associated with cognitive decline in the elderly.

▲Ergothioneine affects epigenetic methylation and demethylation.
The second is skeletal muscle. The unstable gait of the elderly is largely due to oxidative damage to the skeletal muscle, and ergothioneine can help defend against this potential damage. Studies have shown that insufficient intake of ergothioneine may accelerate the aging process and increase the risk of age-related diseases.
Mushrooms are the main dietary source of ergothioneine found so far. If a person does not eat mushrooms often, he or she is likely to lack ergothioneine in the body. Moreover, modern over-cultivation has led to lower and lower levels of ergothioneine in food, so it is a good choice to supplement ergothioneine appropriately through supplements. In terms of safety, the current recommended daily intake of ergothioneine is 30 mg, which is far lower than the no adverse effect intake level (NOAEL) of 800 mg per kilogram of body weight per day set by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has also given ergothioneine “Generally Recognized as Safe” (GRAS) certification, so everyone can use it with confidence.
1. Alpha-Ketoglutarate (AKG)
Mechanism:
- Acts as a key intermediate in the Krebs cycle, enhancing mitochondrial function.
- May promote longevity by inhibiting ATP synthase and reducing mTOR signaling (Chin et al., 2014).
- Supports collagen synthesis, improving skin elasticity.
Evidence:
- Extends lifespan in C. elegans and mice (Sharma et al., 2020).
- Improves age-related metabolic decline (Asadi Shahmirzadi et al., 2020).
2. Pyrroloquinoline Quinone (PQQ)
Mechanism:
- Potent antioxidant that stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis via PGC-1α activation (Chowanadisai et al., 2010).
- Protects against oxidative stress and supports nerve growth factor (NGF) synthesis.
Evidence:
- Enhances cognitive function in aging models (Zhang et al., 2016).
- Improves mitochondrial function in human studies (Harris et al., 2013).
3. Ergothioneine
Mechanism:
- Unique antioxidant with a specific transporter (OCTN1), ensuring cellular uptake (Grundemann et al., 2005).
- Protects against DNA damage and reduces inflammation (Paul & Snyder, 2010).
Evidence:
- Higher levels correlate with reduced cognitive decline (Cheah et al., 2016).
- Shows potential in preventing age-related diseases (Halliwell et al., 2018).
Which Is Superior?
- AKG: Best for metabolic support and lifespan extension.
- PQQ: Best for mitochondrial regeneration and cognitive health.
- Ergothioneine: Best for cellular protection and inflammation control.
Conclusion: The “best” depends on the target—AKG for longevity, PQQ for energy, and ergothioneine for oxidative defense. Combining them may offer synergistic benefits.
References
- Chin, R. M., et al. (2014). Nature Chemical Biology.
- Sharma, A., et al. (2020). Cell Metabolism.
- Chowanadisai, W., et al. (2010). Journal of Biological Chemistry.
- Harris, C. B., et al. (2013). Journal of Medicinal Food.
- Grundemann, D., et al. (2005). PNAS.
- Cheah, I. K., et al. (2016). Redox Biology.
- Halliwell, B., et al. (2018). Biochemical Journal.
Would you like a deeper dive into any specific compound?
