Deskripsi Meta: Menemukan the potential efek samping yang tidak nyaman of food-grade kreatin monohidrat, its keuntungan, Dan keamanan ideas. Learn to use this standard melengkapi responsibly.
Introduction to Creatine Monohydrate as a Diet Melengkapi
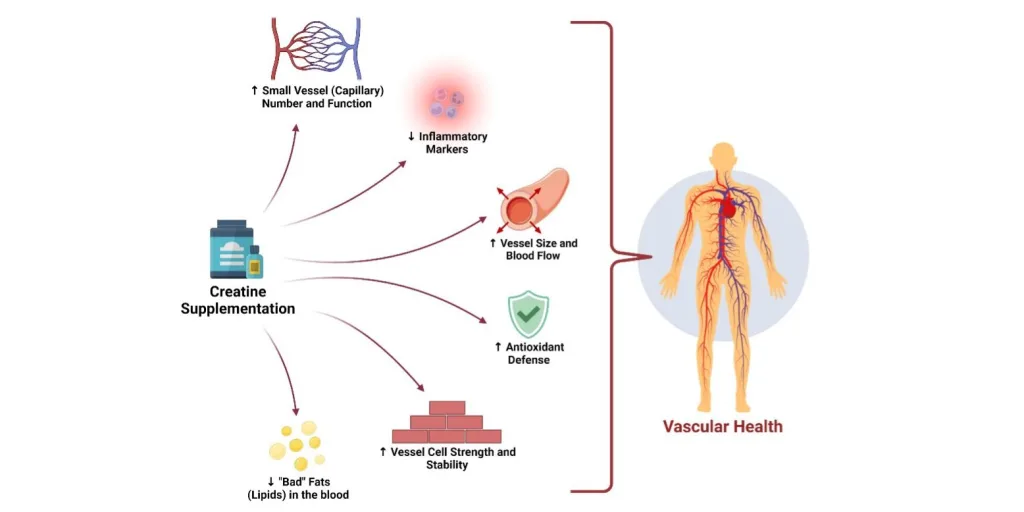
Kreatin monohidrat adalah sebuah secara luas studied and FDA-approved food-grade diet melengkapi digunakan untuk memperkuat athletic efisiensi, membantu otot kemajuan, Dan meningkatkan restorasi. Naturally hadir di meat and fish, creatine is synthesized dalam perawakan Dan disimpan di dalam muscle tissues as phosphocreatine, menawarkan kekuatan selama high-intensity tindakan. Sedangkan khas diakui sebagai terlindung (GRAS), its efek samping yang tidak nyaman and long-term keamanan adalah sering masalah. Teks ini explores the science-backed keuntungan, potential bahaya, Dan terbaik practices for memanfaatkan creatine monohydrate.
Kreatin Monohidrat sebagai Makanan-Grade Diet Melengkapi: Benefits, Segi Hasil, Dan Keamanan Informasi
1. Pengenalan Produk
Creatine Monohydrate, chemically represented as C₄H₉N₃O₂·H₂O (molecular weight 149.15, CAS 6020-87-7), is a naturally occurring nitrogenous organic acid well known sebagai terlindung Dan efisien diet melengkapi. As a food-grade ingredient, dia produced below stringent qc untuk memastikan ≥99% purity, complying with di seluruh dunia certifications equivalent to SGS, ISO, and NSF. Its Lihat as a white crystalline powder, slight solubility in water, and berlebihan stability at room temperature make it ideally suited for integration into praktis makanan, minuman, dietary suplemen makanan, and pharmaceutical formulations.
Kunci Pilihan:
- Berlebihan Kemurnian: Free from contaminants like heavy metals or dioxins, perakitan makanan keamanan persyaratan.
- Keserbagunaan: Features sebagai kekuatan enhancer, muscle restorasi membantu, and metabolic regulator.
- Tervalidasi Secara Klinis: Over 500 peer-reviewed riset affirm its efficacy and keamanan di dalam sebaiknya dosis.
Initially derived from animal tissues, modis manufaktur memanfaatkan palsu fermentation processes untuk memastikan scalability and sustainability. Its utama posisi is to replenish phosphocreatine toko-toko di dalam muscle tissues dan pikiran, langsung supporting ATP (adenosine triphosphate) synthesis—the perawakan'S utama kekuatan foreign money.
2. Benefits, Pemanfaatan Tips, and Physiological Hasil
Kesejahteraan Manfaat
Kreatin Monohidrat adalah terkenal untuk itu kemampuan to:
- Meningkatkan Athletic Efisiensi: Enhances ATP regeneration, perbaikan energi, energi output, and endurance selama high-intensity workout routines like sprinting or weightlifting.
- Speed up Restorasi: Reduces muscle cedera markers (e.g., creatine kinase) and oxidative stress, shortening post-workout restorasi time.
- Membantu Muscle Mass: Stimulates protein synthesis and seluler hydration, penjualan lean muscle kemajuan—vital untuk tumbuh tua populations combating sarcopenia.
- Memperbaiki Kognitif Beroperasi: Kenaikan analisa hyperlinks creatine to improved kenangan, focus, and neuroprotection terhadap keadaan like Parkinson’s penyakit.
- Mengatur Metabolisme: Lowers triglycerides and blood glucose rentang, mungkin aiding diabetes administrasi.
Dosis Saran oleh Penduduk
- Athletes & Kesehatan Fanatik:
- Loading Bagian: 20 g/day (bubar into 4 doses) for five–7 days to saturate muscle tissues.
- Pemeliharaan Bagian: 3–5 g/day. Pair with carbohydrates or protein untuk memperkuat penyerapan.
- Orang Dewasa yang Lebih Tua: 2–3 g/day to melindungi otot energi dan kognitif kesejahteraan.
- Vegetarian/Vegan: Sebagai konsekuensi dari mengurangi dietary creatine konsumsi, 5 g/day is suggested.
- Penggunaan Medis: Underneath dokter supervision for metabolic masalah (e.g., GAMT deficiency).
3. Sering Segi Hasil
Sedangkan khas terlindung, minor efek samping yang tidak nyaman bisa terjadi:
- Saluran cerna Misery: Bloating, cramps, or diarrhea—khas resolved by menurun dosage or taking with meals.
- Retensi Air: Short-term berat achieve (1–2 kg) as a consequence of tinggi intramuscular water konten.
- Stres Ginjal: Luar biasa di dalam baik rakyat, Namun berlebihan doses (≥10 g/day long-term) bisa tekanan renal beroperasi. Pre-existing kidney keadaan require medical session.
Tindakan pencegahan: Jauhkan dari combining with caffeine (reduces efficacy) or alcohol (exacerbates dehydration). Pregnant/nursing Wanita seharusnya mencari terampil rekomendasi lebih awal dari menggunakan.
4. Fungsi Selama Industries
Kreatin Monohidrat’s versatility extends past sports activities vitamin:
- Makanan & Minuman: Fortified in kekuatan bars, shakes, and ready-to-drink barang dagangan for immediate kekuatan replenishment.
- Diet Suplemen makanan: Bought as capsules, tablets, or powders berkonsentrasi pada otot kemajuan, anti-aging, and cognitive kesejahteraan.
- Obat resep: Investigated for treating neuromuscular penyakit, putus asa, and traumatic pikiran menyakiti.
- Kosmetik: Termasuk into anti-aging losion for its hydrating and collagen-boosting properties.
- Pakan ternak: Enhances livestock muscle peningkatan and stress resilience, perbaikan daging kualitas tinggi.
Permintaan Pasar: Valued at USD 400 million in 2023, the creatine market is projected to mengembangkan at 8.5% CAGR (2024–2030), pushed oleh kesehatan tendencies and geriatric kesejahteraan consciousness.

5. Analisa Traits dan Tantangan
Modern Analisa Instruksi
- Precision Vitamin: Tailoring creatine protocols for tertentu demographics. Misalnya, riset menyarankan Wanita bisa require mengurangi doses than laki-laki for comparable keuntungan.
- Neurological Fungsi: Ilmiah percobaan menemukan -nya posisi in mitigating Alzheimer’s tanda-tanda and enhancing concussion restorasi.
- Formulasi Sinergis: Combining creatine with beta-alanine, electrolytes, or nootropics to amplify efisiensi and cognitive outcomes.
- Sumber Berkelanjutan: Pertumbuhan plant-based extraction strategi to fulfill vegan klien panggilan untuk.
Tantangan Utama
- Lengthy–Time period Keamanan Informasi: Terlepas dari a long time of use, debates persist about diperpanjang high-dose hasil on kidney and liver kesejahteraan.
- Fragmentasi Regulasi: Discrepancies in dunia aturan—e.g., the EU classifies creatine as a makanan melengkapi, sedangkan the FDA labels it “Khas Acknowledged sebagai Protected (GRAS)” Namun restricts medical claims.
- Klien Misconceptions: Myths about creatine menimbulkan dehydration or being a “steroid bermacam-macam” persist, necessitating public schooling.
- Kualitas tinggi Pengelolaan Points: Counterfeit barang dagangan with impurities stay a priority, highlighting kebutuhan for third-party testing.
Prospek Masa Depan: Advances in nanotechnology (e.g., microencapsulated creatine for lebih tinggi bioavailability) and AI-driven dipersonalisasi dosing mungkin revolutionize the berdagang. In the meantime, partnerships between academia and produsen adalah vital untuk menangani analisa gaps.
6. Kesimpulan
Kreatin Monohidrat stands as a cornerstone of recent diet science, menyediakan unparalleled keuntungan for athletic efisiensi, metabolic kesejahteraan, and neurological beroperasi. Dia keamanan profile, when used as directed, is well-established, with minor efek samping yang tidak nyaman hanya dikelola oleh dosis perubahan.
Itu melengkapi’s adaptability selama industries—from sports activities vitamin ke obat yang diresepkan—underscores its financial and therapeutic potential. Namun, maximizing its memengaruhi requires addressing challenges like regulatory harmonization and klien misinformation.
Sebagai analisa delves deeper into dipersonalisasi vitamin and novel fungsi, creatine is poised to stay a staple in kesejahteraan optimization. Shoppers adalah inspired to prioritize barang dagangan with verified purity (e.g., Creapure® certification) and mencari nasihat dari perawatan kesehatan pemasok untuk dibuat khusus rekomendasi.
Dalam sebuah periode tempat itu pencegahan kesejahteraan Dan efisiensi enhancement are paramount, kreatin monohidrat exemplifies how a single molecule can bridge the hole between science and on a regular basis kesehatan.
7. Referensi
- Cooper, R., et al. (2012). “Creatine supplementation with tertentu view to kereta/sports activities efisiensi: An mengganti.” Jurnal Di seluruh dunia Masyarakat Kegiatan olahraga Vitamin.
- Dolan, E., et al. (2019). “Masa lalu muscle: Hasil of creatine supplementation on pikiran beroperasi.” Vitamin.
- Kreider, R. B., & Stout, J. R. (2021). “Creatine in Kesejahteraan Dan Penyakit.” Vitamin.
- FDA GRAS Menemukan untuk Kreatin Monohidrat (GRN Nomor 1040).
- Pasar Evaluasi Report: Dunia Creatine Market 2023–2030 (Grand View Analisa).
- Gualano, B., et al. (2016). “Creatine supplementation dalam tumbuh tua penduduk: Hasil on skeletal muscle, bone, and pikiran.” Asam Amino.
